By: Michael Gerbick, President at Young & Associates
Interest rate risk (IRR) is the exposure of a bank or credit union’s current or future earnings and capital to adverse changes in market rates. Management of that risk is critical to community financial institutions and since the pandemic and rates went to zero, due to the rapid pace of change, effective management of that risk has been difficult due to the rapid increase in interest rates.
Navigating Market Volatility: The Role of ALM Models
Most banks and credit unions utilize asset liability management (ALM) models to assist in the modeling of interest rate increases and decreases, typically +/- 400 bp shock scenarios. Similar to the parallel rate shock scenarios of the ALM models designed to identify risk exposure in a rapidly changing rate environment, the Fed raised rates between March 2022 and July 2023 from 0% to 5.25–5.50%.
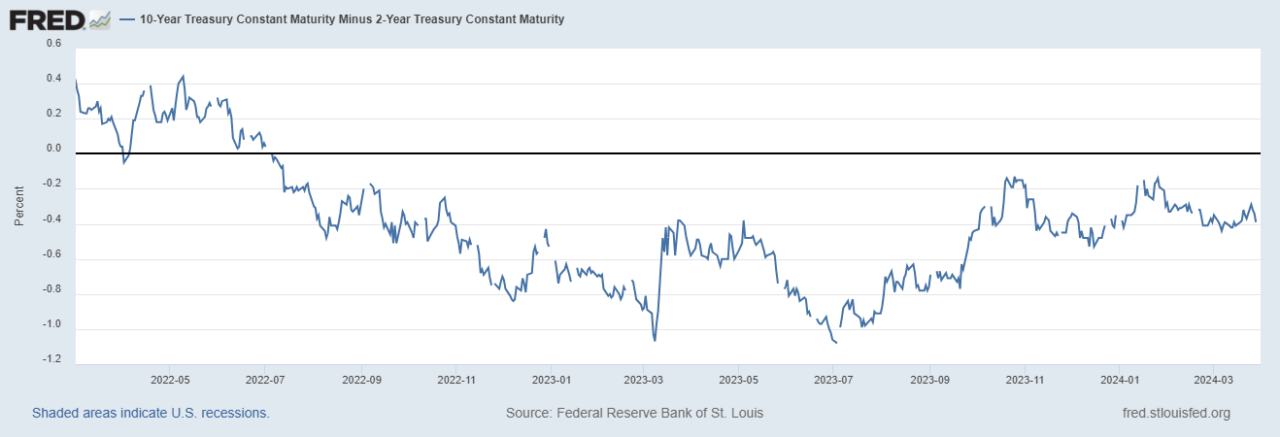
The yield curve shape changed significantly, putting additional stress on the Asset Liability Committees (ALCO) responsible for managing the ALM function of financial institutions, and has not let up. Yes, the inverted yield curve has flattened from 12 months ago, however in March this year, the Treasury yield curve for the two-year and ten-year yields hit a consecutive day record for being inverted 625 days, besting the previous record set in 1978.
The chart shown below1 illustrates the difference between the higher yield 2-year and the lower yield 10-year.
Strategies Amidst Rising Rates: Insights for Community Banks and Credit Unions
Amongst many of the strategies employed during the rising rate environment of 2022 and 2023 was offering certificates of deposit (CDs) to maintain and grow deposits on the balance sheet. However, the funding mix began to shift as consumers migrated towards the higher interest-bearing accounts or the Bank increased Federal Home Loan borrowing which caused the cost of funds to increase.
Industry research for the last two years shows interest-bearing deposits up 5.1% and non-interest-bearing deposits down 28%2. Rates have not risen since July 2023, however many of the CDs offered in 2023 are due to mature in 2024 in a different rate environment than when they were issued. Financial institutions are monitoring this closely.
Strategic Considerations for ALCOs: Addressing Interest Rate Risk
ALCOs are tasked with predicting the interest rate exposure in the elevated rate environment. Currently, we are in a unique environment and banks and credit unions should be cautious about using historical data only to predict future activity. In addition to non-bank competitors competing for deposits, community financial institutions need to continue improving their approach to cost of funds, net interest margin compression, and how the institution will effectively manage their exposure to interest rate risk. A few strategies and actions financial institutions can employ related to deposits are:
Optimizing Interest Rate Exposure
Increase the frequency in which ALCO meets to review the interest rate environment. This may currently be semi-annual or quarterly at your institution. The financial institution may consider meeting monthly to stay abreast of any changes in the environment or new products the Bank is releasing.
Policy Revision
Review your policy limits approved by the Board. Your policy may only have -100 bp or -200 bp scenarios listed given the previous low-rate environment. Not only review the existing policy limits with the Board but increase the stress range to account for -300 bp and -400 bp.
Trigger Points
In addition to the policy limits, consider thresholds for the rate of change of the risk measures that consider risks associated with liquidity, interest rate risk, and capital. These rate of change thresholds are designed to commence action or additional investigation into the source of the significant movement ahead of falling outside of policy limits.
Stress Your Assumptions
ALM models have built-in assumptions and are likely based on historical industry averages supplemented by data supplied by your institution. Common key assumptions outlined by the FDIC3:
- Asset Prepayment – represents the change in cash flows from an asset’s contractual repayment schedule. The severity of prepayments fluctuates with various interest rate scenarios. Mortgage loans are a prime example of assets subject to prepayment fluctuations.
- Non-Maturity Deposits
- Sensitivity or Beta Factor – describes the magnitude of change in deposit rates compared to a driver rate.
- Decay Rate – estimates the amount of existing non-maturity deposits that will run off over time.
- Weighted Average Life – estimates the average effective maturity of the deposits.
- Driver Rate – represents the rate, or rates, which drive the re-pricing characteristics of assets and liabilities. Examples include Fed funds rate, LIBOR, U.S. Treasury yields, and the WSJ Prime rate.
Have discussions with your team and understand what is going on broadly in the economic environment as well as items specific to your bank or credit union. Address changes or concerns in your modeling assumptions or at the very least, be aware of their potential impact. Spend time to learn the assumptions. Do not accept the defaults as correct, make sure your team understands them.
In addition to your base case, stress the assumptions – double or triple the decay rates, assume a high sensitivity to driver rates in the change in deposit rates, and cut the prepayment speeds in half. The alternate scenarios with severe assumptions will assist ALCO in understanding potential value creation and risks.
Interest Rate Risk Review
Regulatory guidance indicates that every bank should have an annual third-party assessment of the interest rate risk system. Similar to other audits, this review should be delivered to the Board of Directors or the Board’s audit committee and is a critical component of the Board’s responsibility for bank oversight.
Educate the Board on Interest Rate Risk
There are educational videos available through the FDIC website. In addition, there are IRR modeling vendors that will attend meetings to provide perspective to your institution on the current economic environment and your modeling results. Leverage them.
Managing Interest Rate Risk in 2024 and Beyond
There is always an opportunity for significant value creation in any environment. The rapidly increasing rate environment experienced in 2022-2023 brought forth significant risks and opportunities. The 2024 environment possesses new challenges, and I am excited to see our community banks and credit unions adjust their balance sheets, act on the highest value opportunities, and limit their interest rate exposure.
Assess Your Interest Rate Risk
Ready to proactively manage your institution’s interest rate risk? Young & Associates offers comprehensive interest rate risk reviews tailored to your needs. Ensure your bank or credit union is prepared to navigate market volatility with confidence. Reach out to us now to schedule your consultation!
1Federal Reserve Economic Data (FRED) 10-Year Treasury Constant Maturity Minus 2-Year Treasury Constant Maturity
2S&P Global US Bank Market Report 2024
3FDIC Developing Key Assumptions for Analysis of Interest Rate Risk